Introduction to Augmented Reality in Medicine
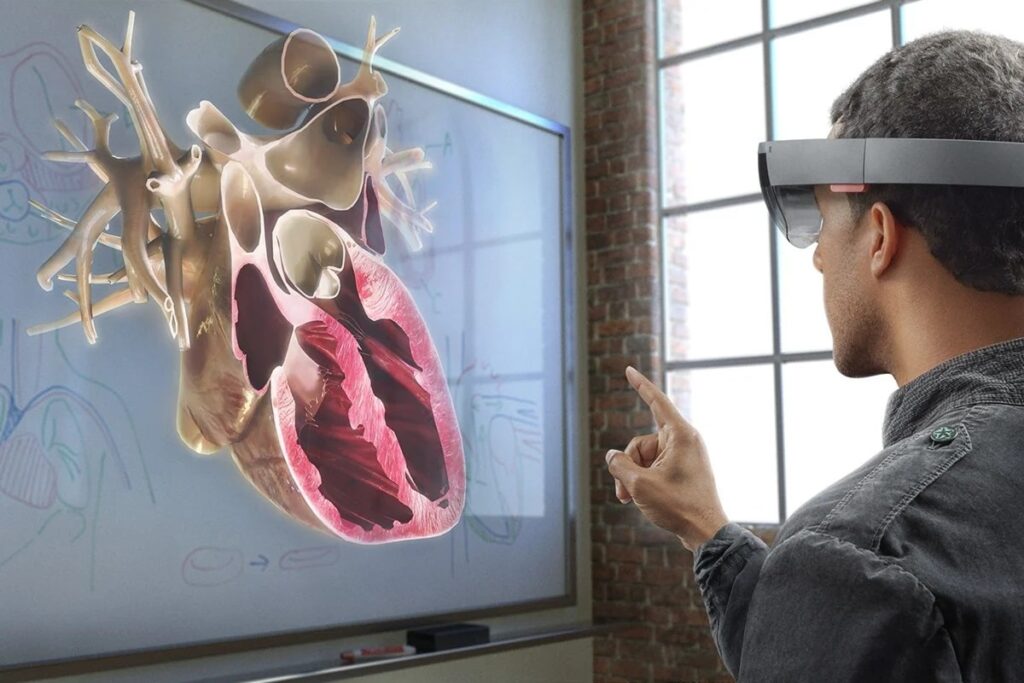
Have you ever worn a pair of Snapchat spectacles or played Pokemon Go? If yes, then you’ve experienced augmented reality (AR). In layperson’s terms, AR overlays virtual information onto the natural world through devices, enhancing our perception of reality. It’s like reading a book and having the characters pop out and enact the scenes right before your eyes!

-
History of Augmented Reality
The concept of AR isn’t new. I mean, really, it’s from the 1960s? The “father of computer graphics,” Ivan Sutherland, invented the “Sword of Damocles,” the first head-mounted display device. Fast forward a few decades, and we’re incorporating AR in fields you’d least expect – like medicine.
Benefits of Augmented Reality in Medicine
-
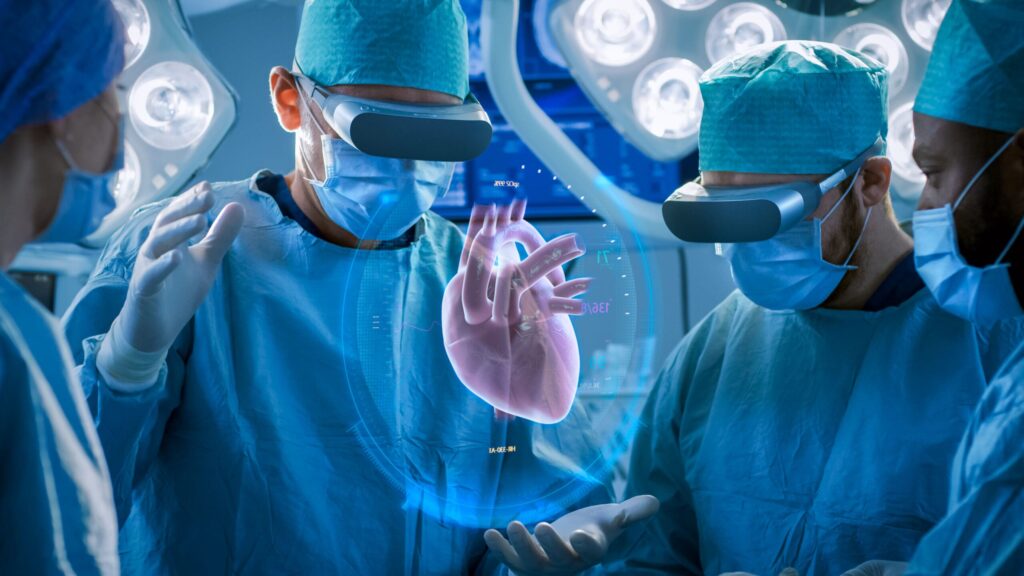
Improved Diagnosis
Remember those complex medical terms and diagrams in textbooks? Imagine having a 3D model of a heart showing you its intricate workings. AR gives medical professionals a 360-degree perspective of a patient’s anatomy, enabling more accurate diagnosis. It’s like watching TV in color instead of black and white—the contrast is fantastic!
-
Enhanced Surgical Procedures
Have you ever tried fixing something using a manual? Now, think of AR as that guide, but for surgeons. AR can project virtual images onto the patient, guiding surgeons during procedures. It’s like having a GPS for surgeries – directing every move!
-
Medical Training and Education
Medical students, remember those sleepless nights with anatomy books? AR can transform those static pages into interactive 3D models. It’s like trading your old bicycle for a brand-new sports car – making learning faster and more efficient.
Challenges of Augmented Reality in Medicine
-
Technical Hurdles
While AR is promising, it’s full of challenges. Reliable tracking, real-time processing, and user interface designs are hurdles yet to be fully overcome. Ever experienced a glitch while playing a video game? Now, imagine that during a surgery. Not so fun, right?
-
Ethical Considerations
Is it ethical to rely heavily on technology, especially when human lives are at stake? While AR can guide, the final decision rests with the human behind the tool. It’s a delicate balance, akin to walking a tightrope.
Current Applications in Medicine
-
Virtual Surgeries
Patients can now preview their surgeries. It’s like watching a trailer before the actual movie, easing anxieties and setting expectations.
-
Patient Education
Doctors can use AR to educate patients about their conditions. It’s similar to using a magnifying glass; things become more transparent and more accessible to understand.
-
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Remember playing ‘Simon Says’? AR in therapy is a bit like that – guiding patients through exercises and ensuring they’re done correctly.
Future of Augmented Reality in Medicine
-
Potential Innovations
From remote surgeries to real-time data analysis during procedures, the sky’s the limit. What if doctors could perform surgeries from miles away, with AR guiding them? Sounds like science fiction, but it might soon be a reality.
-
Ethical and Regulatory Discussions
As AR becomes more prevalent, regulations need to evolve. It’s like updating old laws for modern times, ensuring safety and ethical considerations are met.
Conclusion
Augmented reality in medicine is like the dawn of a new era. It holds the promise of transforming healthcare, making it more efficient, interactive, and precise. While challenges exist, the potential benefits are too significant to ignore. So, are you ready to witness a revolution in healthcare?
FAQs for Augmented Reality in Medicine
Can AR replace traditional medical procedures?
AR is meant to enhance, not replace, traditional methods. It offers guidance and improved visualization but doesn’t replace the expertise of medical professionals.
Is AR in medicine safe?
As with any technology, the safety of AR depends on its application and usage. In medicine, rigorous testing and validation are crucial.
How can patients benefit from AR?
Patients can receive a clearer understanding of their conditions, preview surgical procedures, and even use AR for guided rehabilitation exercises.
Will AR make healthcare more expensive?
Initially, the cost of implementing AR might be high, but in the long run, it can lead to more efficient procedures and reduced hospital stays, potentially saving costs.
Rate our Article (Augmented Reality in Medicine | A Comprehensive Guide)How much do you like our Article?





